Peanuts - Intermediate
Nitrogen Fixation
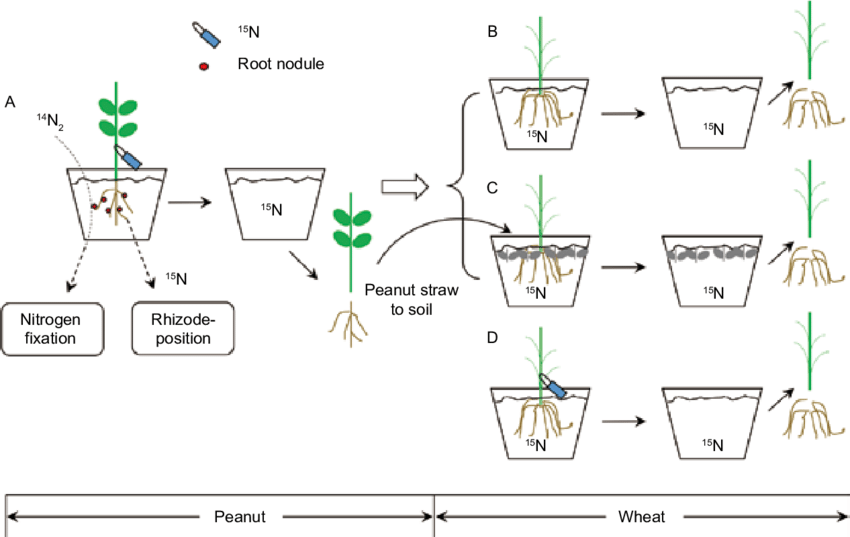
Nitrogen fixation is the process by which atmospheric nitrogen gas is converted into a biologically useful form by certain bacteria, and it is an important process for plant growth. In the case of peanuts, specific bacteria form a symbiotic relationship with the plant and reside in specialized root nodules, where they convert nitrogen gas into ammonia. The ammonia is then used by the plant for various cellular processes, including protein synthesis and DNA replication, which are essential for growth and development. This relationship between the plant and the nitrogen-fixing bacteria is important for sustainable agriculture, as it reduces the need for synthetic fertilizers and promotes soil health.